|
| you are here > Class Notes - Chapter 11 - Lesson 11-5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
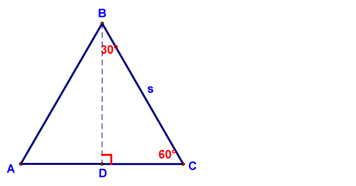
Areas of Regular Polygons - Lesson 11-5 Today we started by deriving a formula for the area of an equilateral (regular) triangle. If you start with an equilateral triangle with side length s:
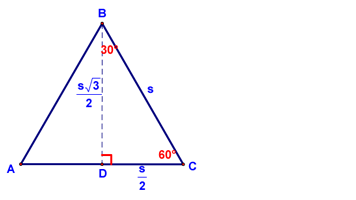
And then do the standard procedure for finding the length of the altitude (love those 30-60-90 triangles!),
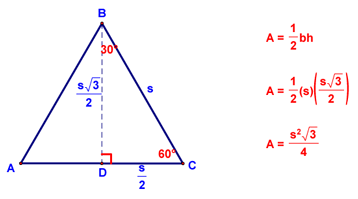
you are then able to use the formula for the area of a triangle to derive a new formula
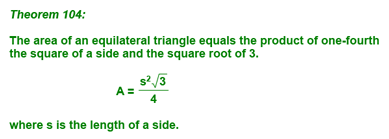
which can be summarized as follows:
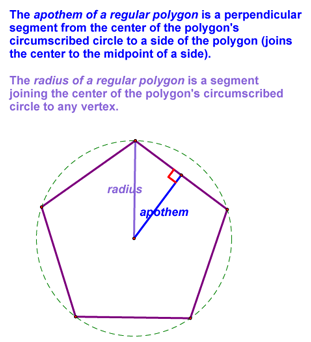
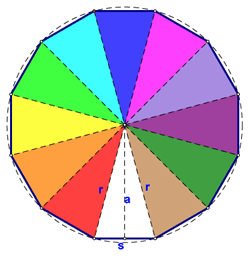
Next, we can generalize an area formula for all regular polygons. To start, we need to define the radius and the apothem of a regular polygon:
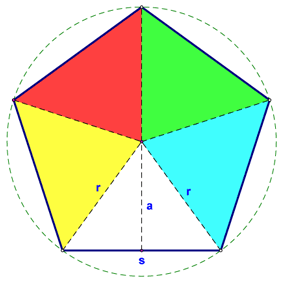
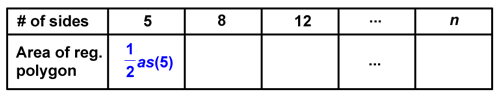
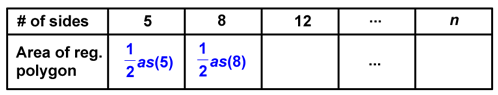
If we look at a pentagon, you should be able to see how the formula for its area would be as shown in the table below:
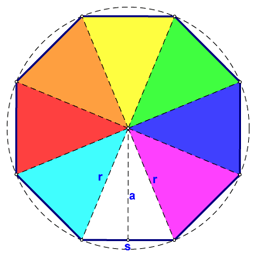
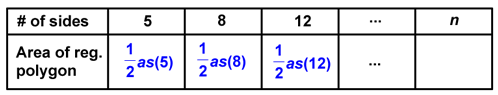
The same can be said for an octagon
and a dodecagon.
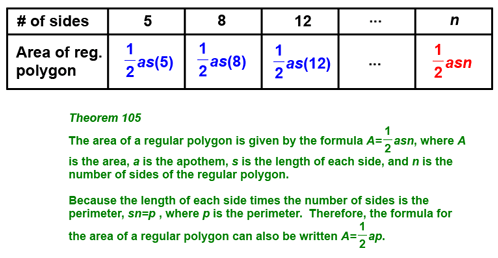
In conclusion, we can derive the general formula to find the area of any given regular polygon:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||